Guide to Laboratory Shakers
Dec 6th 2024
Laboratory shakers are indispensable pieces of equipment across various scientific disciplines, enabling the efficient agitation or mixing of substances. From biology and chemistry to medicine and environmental science, they play a crucial role in ensuring consistency, accelerating reactions, and optimizing conditions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of shakers, including their types, applications, and guidance on selecting the right model for specific lab applications.
What Are Laboratory Shakers?
A laboratory shaker is a device used to agitate liquids, powders, or cell cultures within a container, ensuring uniform distribution of substances. Shakers facilitate a range of processes, from mixing solutions and enhancing chemical reactions to culturing cells and extracting biomolecules. By enabling consistent and controlled agitation, shakers help improve the precision, reproducibility, and efficiency of scientific experiments.
There are several shaker types to choose from, each with their own shaking mechanism, mixing speeds and motions. Let's dive into the different types of lab shakers further.
Types of Lab Shakers
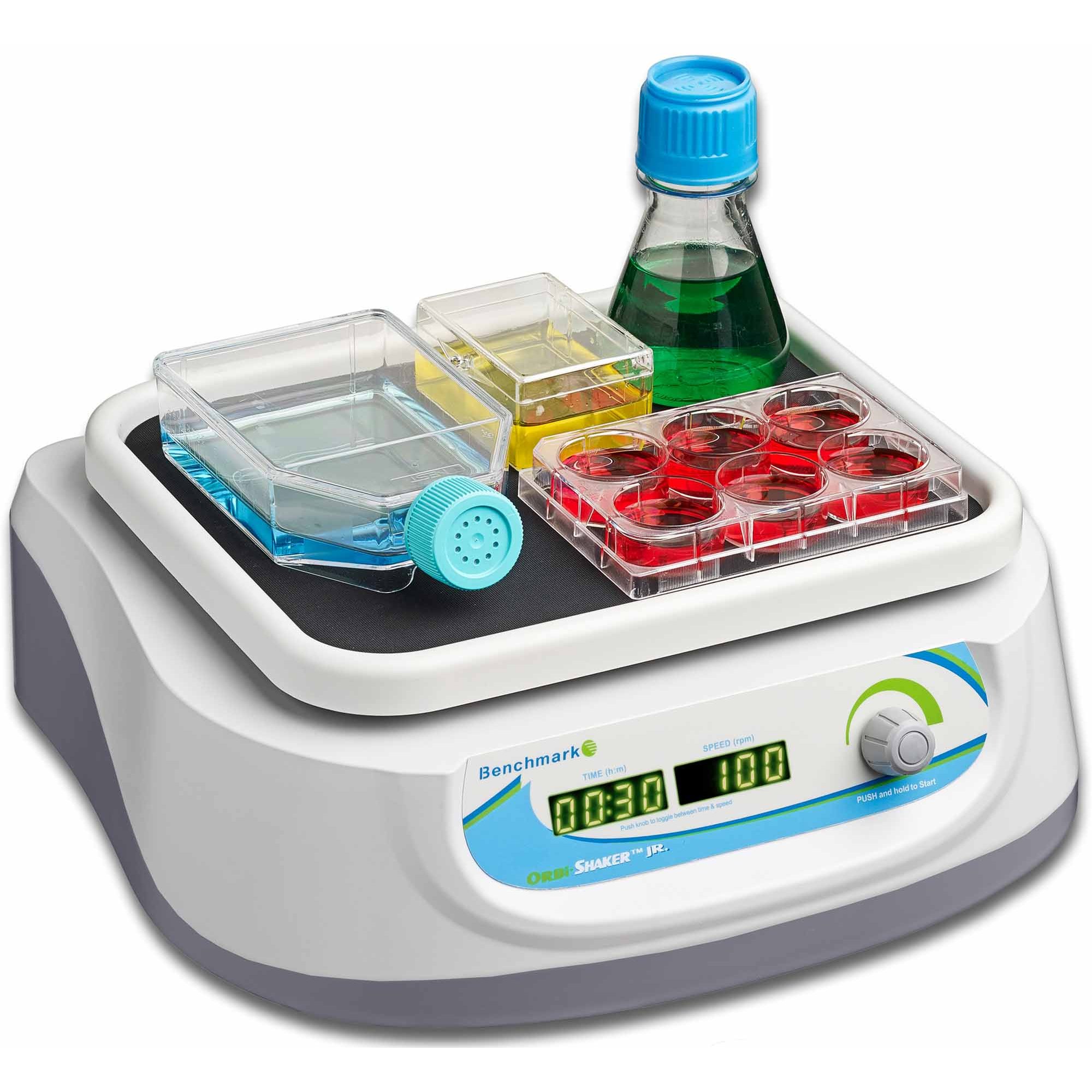
Orbital Shakers
- Mechanism: Also referred to as orbital mixers, these shakers create a circular, orbital motion to agitate the contents of containers placed on the platform.
- Applications: Orbital shakers are widely used for mixing liquids in flasks, bottles, microplates, test tubes and other vessels. They are particularly suited for tasks such as culturing cells, preparing chemical solutions, and promoting uniform mixing of reagents.
- Advantages: They offer a smooth and consistent agitation, making them ideal for biological and chemical applications that require gentle yet continuous mixing.
Vortex Mixers
- Mechanism: Vortex mixers are a type of shaker that generate a rapid, localized swirling motion at the surface of the liquid, creating a vortex effect.
- Applications: These are commonly used for rapidly mixing small samples in test tubes, vials, or microcentrifuge tubes. They are especially useful for tasks like resuspending precipitates, mixing DNA or RNA samples, or quickly blending small volumes.
- Advantages: The vigorous, fast agitation is ideal for thoroughly mixing small amounts of sample, but it may not be appropriate for more sensitive applications requiring gentle agitation.

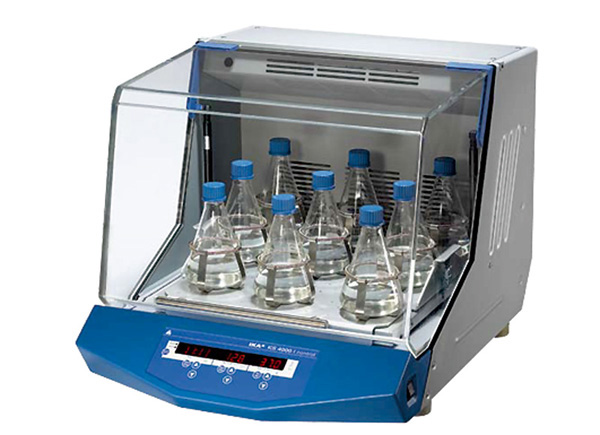
Incubator Shakers
- Mechanism: Incubator shakers combine the functionality of an orbital shaker with precise temperature control, providing both agitation and environmental regulation.
- Applications: Often used in microbiology, cell culture, and biochemical experiments, incubator shakers maintain optimal growth conditions by providing temperature regulation alongside gentle shaking. They come in a variety of sizes and capacities, accommodating both small and large vessels like flasks and bottles.
- Advantages: The ability to control both temperature and agitation makes these shakers ideal for experiments that require sustained, controlled conditions, such as bacterial growth or protein expression.

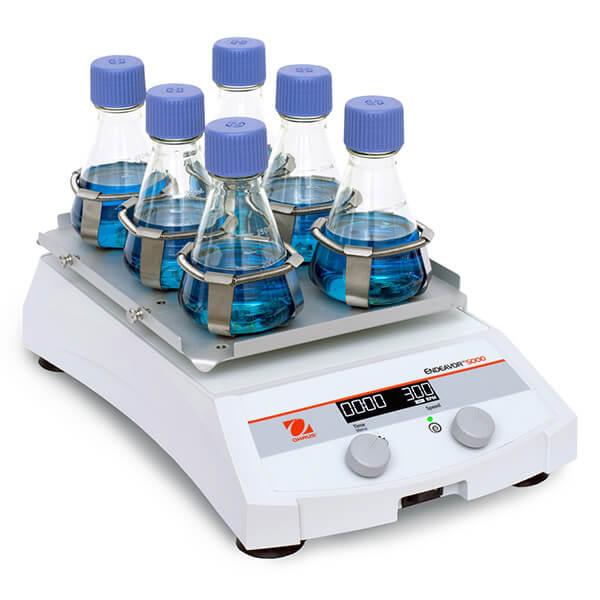
Platform Shakers
- Mechanism: These shakers feature a flat, stable platform where multiple vessels can be placed and shaken simultaneously. The motion can be either linear or orbital, depending on the design.
- Applications: Platform shakers are used in applications where multiple samples need to be processed at once, such as in large-scale mixing of solutions or batch processing of liquid cultures. They are commonly used for shaking flasks, bottles, beakers and other vessels.
- Advantages: Their ability to accommodate multiple vessels makes them particularly useful in high-throughput environments or when large volumes need to be agitated simultaneously.
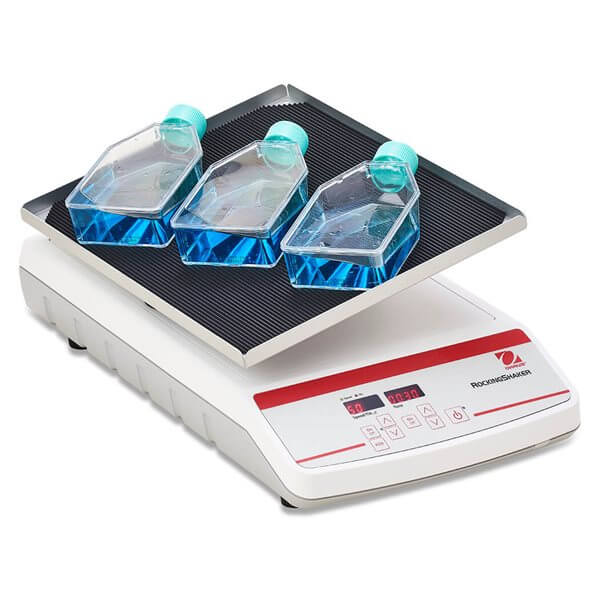
Rockers
- Mechanism: Rockers are a type of shaker that provide a gentle tilting or rocking motion, which is ideal for mixing samples without creating turbulent agitation.
- Applications: These are typically used for applications requiring gentle mixing, such as blood sample handling, DNA purification, or mixing sensitive reagents. Cell culture flasks, bottles and tubes are all common vessels used for mixing with rockers.
- Advantages: The gentle rocking motion prevents damage to delicate samples, such as cells or fragile proteins, making it suitable for more sensitive biological processes.

How Shakers are Used in Labs
Lab shakers are employed across a variety of scientific and industrial applications. Below, we explore some of the common uses and the reasons why they are critical for these processes.
Mixing Solutions
Shakers are essential for thoroughly blending different substances, ensuring uniformity in chemical reactions or solution preparation. Whether dissolving salts in water, mixing reagents for a chemical assay, or preparing buffers for experiments, shaking ensures that all components are evenly distributed.
- Why it matters: Inconsistent mixing can lead to inaccurate results or failed experiments. For instance, when preparing solutions with specific concentrations, uniform mixing ensures that all parts of the solution have the correct properties.
- Recommended: Orbital or platform shakers provide consistent and gentle agitation to achieve homogeneous solutions. Vortex mixers may also be used for quick, vigorous mixing tasks.
Culturing Cells and Microorganisms
In biological research, shaking is crucial for maintaining cells or microorganisms in suspension. Continuous agitation promotes aeration, ensuring cells receive the oxygen needed for growth while preventing clumping.
- Why it matters: Without proper agitation, cells can settle at the bottom of flasks, limiting their exposure to nutrients and oxygen. This can result in uneven growth and unreliable experimental results.
- Recommended: Incubator shakers are particularly useful for culturing cells or microorganisms, as they combine shaking with temperature control, enabling precise growth conditions.
Accelerating Chemical Reactions
Mixing enhances the speed of certain chemical reactions by increasing the interaction between reactants. This is particularly important in reactions involving solids, as agitation can help break down particles and increase the available surface area for reactions to occur.
- Why it matters: Faster reactions allow for more efficient use of time and resources. In applications like enzyme assays, the reaction speed can directly affect the reliability of the results.
- Recommended: Orbital shakers, which provide consistent, moderate agitation, are commonly used to accelerate reactions. For more intense agitation, a vortex mixer may be appropriate.
Homogenizing Samples
In many experiments, samples need to be homogenized to ensure that they are uniform throughout. This is crucial when preparing samples for analysis, as inconsistencies can lead to incorrect data.
- Why it matters: Homogenization ensures that test samples, such as liquids or suspensions, are consistent, which is essential for reliable results, especially when measuring concentrations of chemical substances or biological markers.
- Recommended: Orbital shakers are ideal for this purpose, as they can handle a range of sample types and volumes, ensuring thorough and consistent mixing.
Protein and DNA Extraction
Shaking is integral to the extraction of proteins, DNA, RNA, and other biomolecules. It helps break open cells, release the desired molecules, and ensure thorough mixing of the extraction buffer and biological material.
- Why it matters: Incomplete cell lysis or uneven mixing can result in low yields or contamination of the extracted material, potentially impacting downstream analyses like PCR, electrophoresis, or protein assays.
- Recommended: Orbital or platform shakers are typically used for this process, as they provide consistent agitation without disrupting the integrity of the extracted biomolecules.
Extracting Compounds from Solid Materials
Shakers are also used in solid-liquid extraction processes, where compounds such as oils, flavors, or chemicals need to be extracted from solid materials like plants or seeds. Agitation aids in the efficient transfer of compounds into the solvent.
- Why it matters: Efficient extraction is critical for obtaining a high yield of the desired compound. Inconsistent shaking can lead to incomplete extraction, which could affect the purity and concentration of the extracted material.
- Recommended: Orbital and platform shakers are commonly employed for solid-liquid extractions, as they allow for efficient mixing of large volumes or multiple samples.
How to Choose the Right Shaker
When selecting a shaker, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets the specific requirements of your experiment:
Sample Type and Volume: Consider the size and quantity of samples. Small volumes may require a vortex shaker, while larger volumes or multiple samples may be better handled with orbital or platform shakers with a larger working surface.
Required Shaking Motion: Different motions (orbital, linear, rocking) suit different tasks. Orbital shakers are ideal for gentle, consistent agitation, while vortex shakers provide vigorous mixing for small samples.
Available Accessories: Many shakers offer an assortment of accessories, designed to accommodate a wide range of vessels. Make sure the shaker you choose offers the appropriate platform, clips, clamps or other attachment devices to work with your specified containers.
Temperature Control: For temperature-sensitive applications, such as cell culturing or enzyme reactions, a shaker with integrated temperature control is necessary.
Speed Range and Control: Some experiments require high-speed mixing, while others need slow, controlled agitation. Ensure the shaker you choose offers the necessary speed settings.
Space and Noise Levels: If space is limited or noise is a concern in your laboratory, choose a shaker that fits your workspace and operates quietly.
Conclusion
Shakers are essential lab equipment for efficient and accurate scientific research, offering a wide range of applications, from mixing solutions and accelerating chemical reactions to culturing cells and extracting biomolecules. Understanding the types of shakers available, their specific applications, and how to choose the right model for your needs will help ensure your experiments are conducted with precision and consistency.

